CONFIDENTIALITY, INTEGRITY AND AVAILABILITY
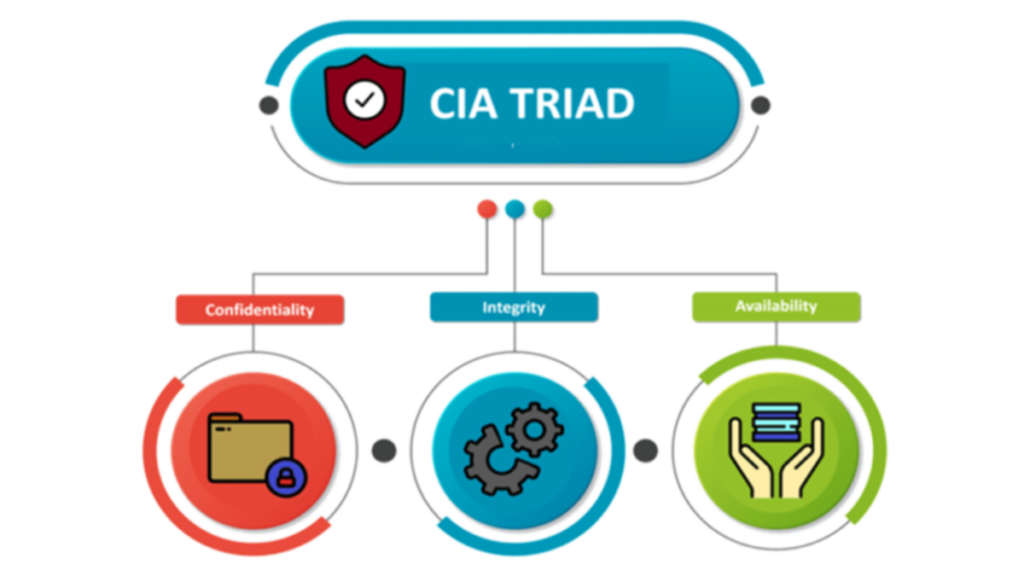
The well-known CIA Triad of confidentiality, integrity and availability is considered the core underpinning of information security. Every security control and every security vulnerability can be viewed in light of one or more of these key concepts. For a security program to be considered comprehensive and complete, it must adequately address the entire CIA Triad.
WHAT IS THE CONFIDENTIALITY, INTEGRITY AND AVAILABILITY (CIA) TRIAD?
CIA TRIAD
Confidentiality means that data, objects and resources are protected from unauthorized viewing and other access. Integrity means that data is protected from unauthorized changes to ensure that it is reliable and correct. Availability means that authorized users have access to the systems and the resources they need.
If you are preparing for the CISSP, Security+, CySA+, or another security certification exam, you will need to have an understanding of the importance of the CIA Triad, the definitions of each of the three elements, and how security controls address the elements to protect information systems.
HOW FREQUENT DO FINGERPRINTS CHANGE?
WHAT IS CONFIDENTIALITY?
WHAT IS CONFIDENTIALITY
Confidentiality measures protect information from unauthorized access and misuse. Most information systems house information that has some degree of sensitivity. It might be proprietary business information that competitors could use to their advantage, or personal information regarding an organization’s employees, customers or clients.
Confidential information often has value and systems are therefore under frequent attack as criminals hunt for vulnerabilities to exploit. Threat vectors include direct attacks such as stealing passwords and capturing network traffic, and more layered attacks such as social engineering and phishing. Not all confidentiality breaches are intentional. A few types of common accidental breaches include emailing sensitive information to the wrong recipient, publishing private data to public web servers, and leaving confidential information displayed on an unattended computer monitor.
HOW MUCH SECURITY DOES A RETINAL SCAN OFFER?
WHAT ARE THE RISKS THAT CAN AFFECT CONFIDENTIALITY?
- Data encryption
- Packet sniffing
- Password cracking
- Dumpster diving
- Wiretapping
- Keylogging
- Phishing
- Ways to ensure confidentiality
- Usernames and passwords
- Two-factor authentication
- Biometric verification
- Security tokens or key fobs
COUNTERMEASURES
There are many countermeasures that organizations put in place to ensure confidentiality. Passwords, access control lists and authentication procedures use software to control access to resources. These access control methods are complemented by the use encryption to protect information that can be accessed despite the controls, such as emails that are in transit. Additional confidentiality countermeasures include administrative solutions such as policies and training, as well as physical controls that prevent people from accessing facilities and equipment.
THE BEST INFORMATION SECURITY AUDIT CHECKLIST TO HELP YOU THRIVE
WHAT IS INTEGRITY?

WHAT IS INTEGRITY
In the CIA Triad of confidentiality, integrity, and availability, Integrity measures protect information from unauthorized alteration. These measures provide assurance in the accuracy and completeness of data. The need to protect information includes both data that is stored on systems and data that is transmitted between systems such as email. In maintaining integrity, it is not only necessary to control access at the system level, but to further ensure that system users are only able to alter information that they are legitimately authorized to alter.
As with confidentiality protection, the protection of data integrity extends beyond intentional breaches. Effective integrity countermeasures must also protect against unintentional alteration, such as user errors or data loss that is a result of a system malfunction.
WHAT ARE THE ATTACKS THAT CAN AFFECT INTEGRITY?
- Any type of Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack
- Salami attack
- Session hijacking
- Data diddling attacks
COUNTERMEASURES
There are many countermeasures that can be put in place to protect integrity. Access control and rigorous authentication can help prevent authorized users from making unauthorized changes. Hash verifications and digital signatures can help ensure that transactions are authentic and that files have not been modified or corrupted. Equally important to protecting data integrity are administrative controls such as separation of duties and training.
WHAT IS AVAILABILITY?
WHAT IS AVAILABILITY
In order for an information system to be useful it must be available to authorized users. Availability measures protect timely and uninterrupted access to the system. Some of the most fundamental threats to availability are non-malicious in nature and include hardware failures, unscheduled software downtime and network bandwidth issues. Malicious attacks include various forms of sabotage intended to cause harm to an organization by denying users access to the information system.
The availability and responsiveness of a website is a high priority for many business. Disruption of website availability for even a short time can lead to loss of revenue, customer dissatisfaction and reputation damage. The Denial of Service (DoS) attack is a method frequently used by hackers to disrupt web service. In a DoS attack, hackers flood a server with superfluous requests, overwhelming the server and degrading service for legitimate users. Over the years, service providers have developed sophisticated countermeasures for detecting and protecting against DoS attacks, but hackers also continue to gain in sophistication and such attacks remain an ongoing concern.
WHAT ARE THE RISKS THAT CAN AFFECT AVAILABILITY?
- Any Physical attacks on server infrastructure
- DoS and DDoS attacks
- SYN flood attacks
COUNTERMEASURES
Availability countermeasures to protect system availability are as far ranging as the threats to availability. Systems that have a high requirement for continuous uptime should have significant hardware redundancy with backup servers and data storage immediately available. For large, enterprise systems it is common to have redundant systems in separate physical locations. Software tools should be in place to monitor system performance and network traffic. Countermeasures to protect against DoS attacks include firewalls and routers.
WHAT IS INFORMATION RISK MANAGEMENT? UNDERSTAND IT BETTER!
THE BOTTOM LINE
Understanding the CIA Triad of confidentiality, integrity, and availability is pretty important as it holds a crucial component of your preparation for a variety of security certification programs. For further information or similar blogs, feel free to visit Securityx anytime, anywhere!

0 Comments